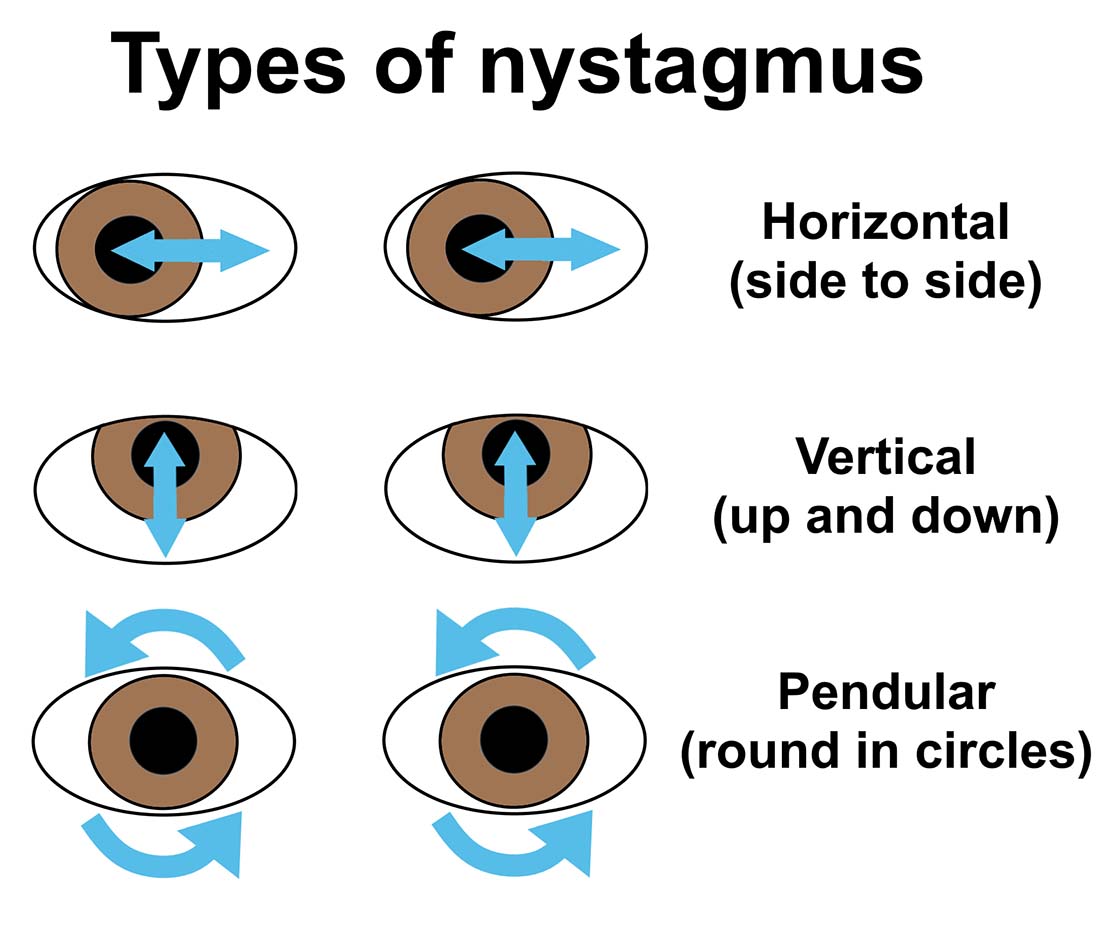
Binocular Nystagmus . nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is in motion. nystagmus is an involuntary, rapid, rhythmic, oscillatory eye movement with at least 1 slow phase. — nystagmus represents uncontrolled, repetitive movements of the eyes. — nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social life. Pendular nystagmus has only slow phases. Jerk nystagmus has a slow phase and a fast phase. Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory eye movements, such as saccadic intrusions or oscillations. Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target followed by a second. Infantile nystagmus (in) is much. Nystagmus may be monocular (in one eye) or binocular (in both eyes).
from www.pdsa.org.uk
— nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social life. Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory eye movements, such as saccadic intrusions or oscillations. Nystagmus may be monocular (in one eye) or binocular (in both eyes). Infantile nystagmus (in) is much. nystagmus is an involuntary, rapid, rhythmic, oscillatory eye movement with at least 1 slow phase. — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target followed by a second. nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is in motion. — nystagmus represents uncontrolled, repetitive movements of the eyes. Pendular nystagmus has only slow phases. Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or.
Nystagmus (flickering eye movements) in a dog PDSA
Binocular Nystagmus — nystagmus represents uncontrolled, repetitive movements of the eyes. Jerk nystagmus has a slow phase and a fast phase. Nystagmus may be monocular (in one eye) or binocular (in both eyes). — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target followed by a second. Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory eye movements, such as saccadic intrusions or oscillations. — nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social life. — nystagmus represents uncontrolled, repetitive movements of the eyes. nystagmus is an involuntary, rapid, rhythmic, oscillatory eye movement with at least 1 slow phase. Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is in motion. Infantile nystagmus (in) is much. Pendular nystagmus has only slow phases.
From www.slideshare.net
Nystagmus Binocular Nystagmus — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target followed by a second. nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is in motion. Jerk nystagmus has a slow phase and a fast phase. Pendular nystagmus has only slow phases. Nystagmus. Binocular Nystagmus.
From archopht.jamanetwork.com
Latent Nystagmus Ophthalmology JAMA Ophthalmology The JAMA Network Binocular Nystagmus — nystagmus represents uncontrolled, repetitive movements of the eyes. nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is in motion. Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory eye movements, such as saccadic intrusions or oscillations. Infantile nystagmus (in) is much. nystagmus is an involuntary, rapid, rhythmic, oscillatory eye movement with. Binocular Nystagmus.
From jamanetwork.com
Latent Nystagmus Vestibular Nystagmus With a Twist Ophthalmology Binocular Nystagmus Nystagmus may be monocular (in one eye) or binocular (in both eyes). Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. nystagmus is an involuntary, rapid, rhythmic, oscillatory eye movement with at least 1 slow phase. — nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social life. Nystagmus is distinguished from. Binocular Nystagmus.
From samarpanphysioclinic.com
CRANIAL NERVE 3,4 AND 6 SAMARPAN PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC AHMEDABAD Binocular Nystagmus Jerk nystagmus has a slow phase and a fast phase. Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. Nystagmus may be monocular (in one eye) or binocular (in both eyes). nystagmus is an involuntary, rapid, rhythmic, oscillatory eye movement with at least 1 slow phase. Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.slideshare.net
Nystagmus Binocular Nystagmus — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target followed by a second. — nystagmus represents uncontrolled, repetitive movements of the eyes. Nystagmus may be monocular (in one eye) or binocular (in both eyes). — nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Monocular and Binocular Visual Function Deficits in Amblyopic Binocular Nystagmus Nystagmus may be monocular (in one eye) or binocular (in both eyes). — nystagmus represents uncontrolled, repetitive movements of the eyes. — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target followed by a second. Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory eye movements, such as saccadic. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) The Role of Attention in Binocular Rivalry as Revealed Through Binocular Nystagmus — nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social life. Pendular nystagmus has only slow phases. Infantile nystagmus (in) is much. Jerk nystagmus has a slow phase and a fast phase. Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.oscarwylee.com.au
Nystagmus Definition, Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Binocular Nystagmus — nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social life. Pendular nystagmus has only slow phases. Nystagmus may be monocular (in one eye) or binocular (in both eyes). — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target followed by a second. Nystagmus is distinguished. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.pdsa.org.uk
Nystagmus (flickering eye movements) in a dog PDSA Binocular Nystagmus nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is in motion. Infantile nystagmus (in) is much. Pendular nystagmus has only slow phases. — nystagmus represents uncontrolled, repetitive movements of the eyes. — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.slideshare.net
Nystagmus Binocular Nystagmus Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. Jerk nystagmus has a slow phase and a fast phase. Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory eye movements, such as saccadic intrusions or oscillations. nystagmus is an involuntary, rapid, rhythmic, oscillatory eye movement with at least 1 slow phase. — nystagmus is. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 1 from Threedimensional binocular kinematics of torsional Binocular Nystagmus Pendular nystagmus has only slow phases. nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is in motion. Infantile nystagmus (in) is much. Nystagmus may be monocular (in one eye) or binocular (in both eyes). Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory eye movements, such as saccadic intrusions or oscillations. Nystagmus can be. Binocular Nystagmus.
From in.pinterest.com
Nystagmus can be inherited or can develop later in life. It may be due Binocular Nystagmus Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is in motion. — nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social life. Pendular nystagmus has only slow phases. nystagmus is an involuntary, rapid, rhythmic, oscillatory. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.semanticscholar.org
Figure 2 from Threedimensional binocular kinematics of torsional Binocular Nystagmus — nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social life. Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory eye movements, such as saccadic intrusions or oscillations. nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.researchgate.net
Nystagmus waveform ranges for all three subjects demonstrating the Binocular Nystagmus nystagmus is an involuntary, rapid, rhythmic, oscillatory eye movement with at least 1 slow phase. Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is in motion. Nystagmus may be monocular (in one eye) or binocular (in both eyes).. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.researchgate.net
Binocular videooculographic recording during straightahead fixation Binocular Nystagmus — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target followed by a second. Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory eye movements, such as saccadic intrusions or oscillations. Infantile nystagmus (in) is much. — nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social life.. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.visioncenter.org
Nystagmus What Is It and When To Get Tested? Binocular Nystagmus Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. nystagmus is an involuntary, rapid, rhythmic, oscillatory eye movement with at least 1 slow phase. Jerk nystagmus has a slow phase and a fast phase. — nystagmus represents uncontrolled, repetitive movements of the eyes. — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements. Binocular Nystagmus.
From www.researchgate.net
Patient 1. Eye movement recordings showing microstrabismus and Binocular Nystagmus nystagmus is an aberration in this stabilization of the ocular muscles when the head is in motion. Pendular nystagmus has only slow phases. Nystagmus can be congenital (ie, noted in the first 6 months of life) or. — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target followed. Binocular Nystagmus.
From youtube.com
Nystagmus, An Introduction YouTube Binocular Nystagmus — nystagmus is defined by rhythmic, abnormal eye movements with a slow eye movement driving the eye off the target followed by a second. Nystagmus is distinguished from other types of oscillatory eye movements, such as saccadic intrusions or oscillations. — nystagmus has a profound impact on patients visual function and social life. Infantile nystagmus (in) is much.. Binocular Nystagmus.